How are tariffs calculated and what role does the tariff basis play?
To successfully accomplish the desired calculations with tariffs, the basis of the tariff is a decisive factor. This article provides you with selected, practice-oriented examples using different bases.
The following bases are explained in more detail in this article using a practical example:
- Base amount only
- Chargeable Weight
- Positions in customs declaration
- Container Type
- Amount Charge Type (Costs)
- Amount Charge Type List (Costs)
- Manual Entry
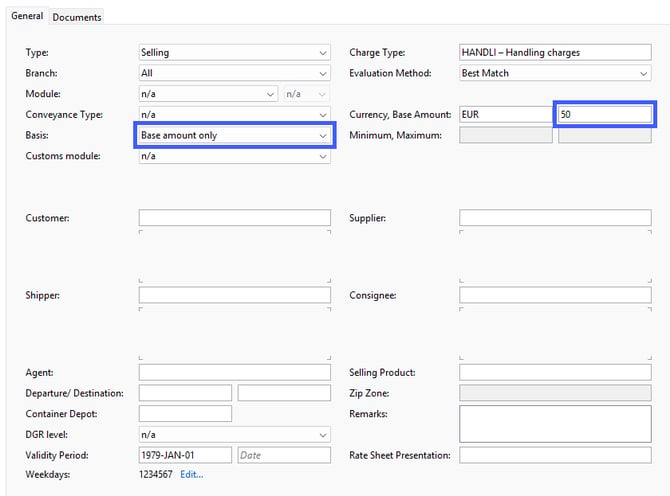
Basis: Base amount only
Example: You want to charge your customer a standard fee of 50.00 EUR for the cost type Handling.
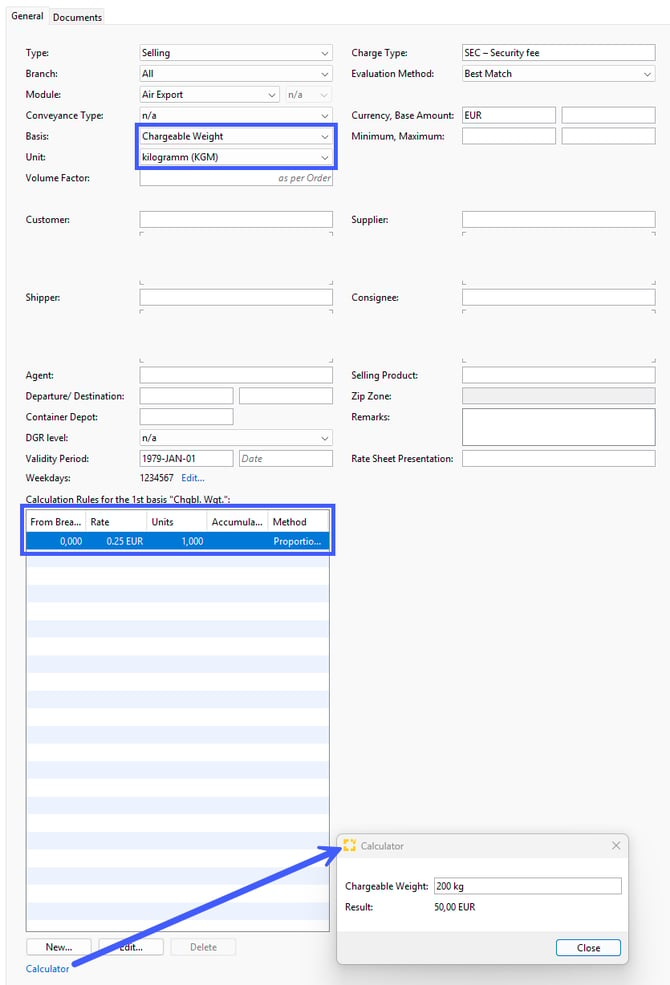
Basis: Chargeable Weight
Example: You want to charge your customer the security fee by chargeable weight at a rate of 0.25 EUR per kg.
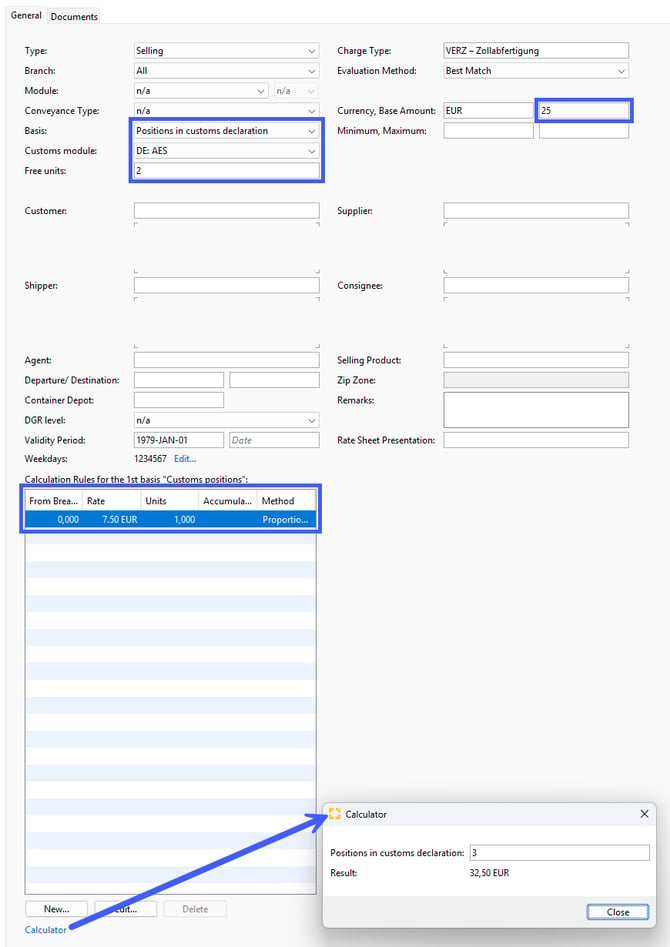
Basis: Positions in customs declaration
Beispiel: You want to charge your customer for the customs declaration in the module AES a base amount of 25.00 EUR, including 2 free positions and for each additional position another 7.50 EUR.
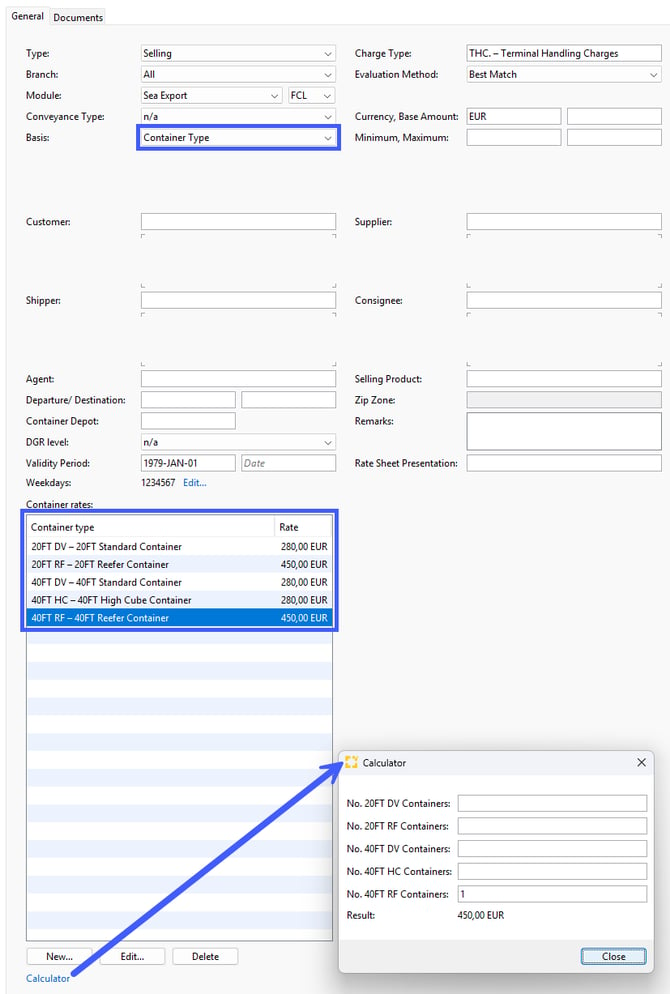
Basis: Container Type
Example: You want to charge your customer THC (Terminal Handling Charge) for all dry container at a rate of 280.00 EUR and for reefer container 450.00 EUR.
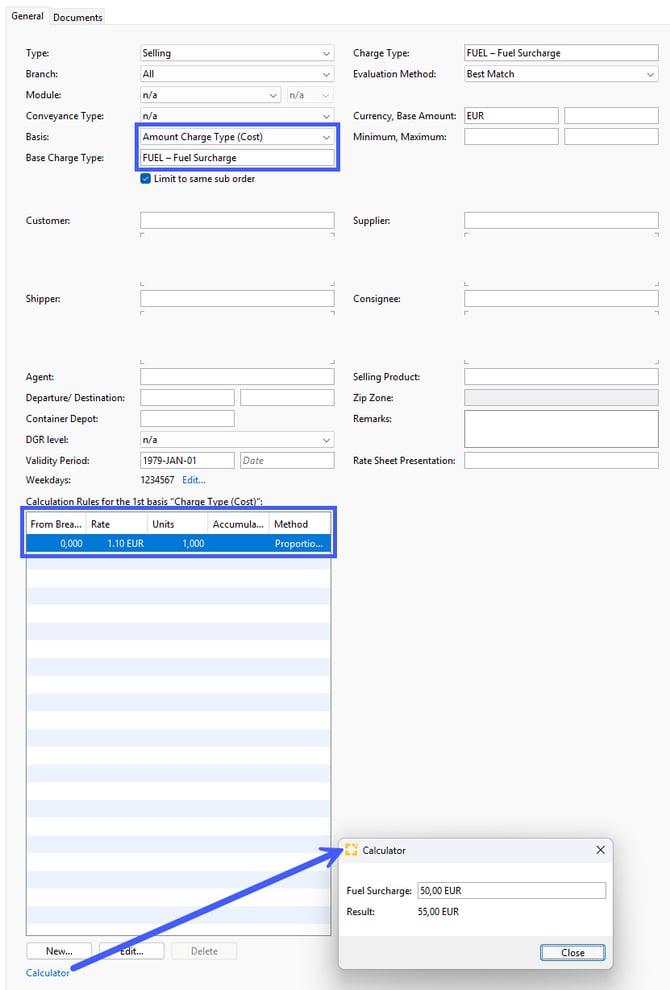
Basis: Amount Charge Type (Cost)
Example: Your selling rate for the fuel surcharge shall be 10% on top of the buying rate of the fuel surcharge.
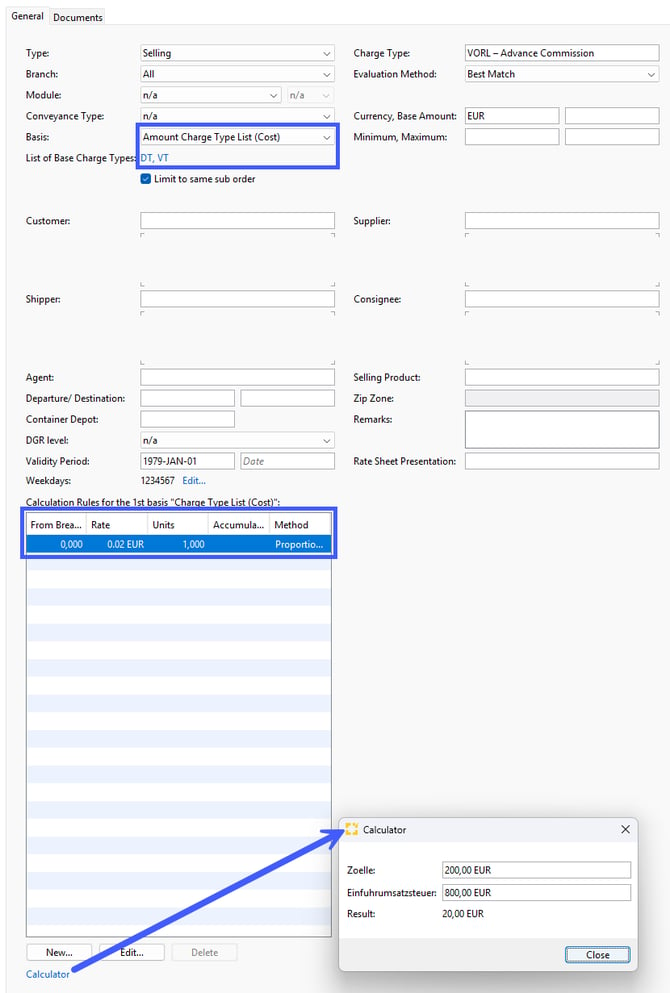
Basis: Amount Charge Type List (Cost)
Example: You want to charge your customer the advance commission at a rate of 2% based on the sum of the costs of DT = Import Duties and VT = Import VAT.
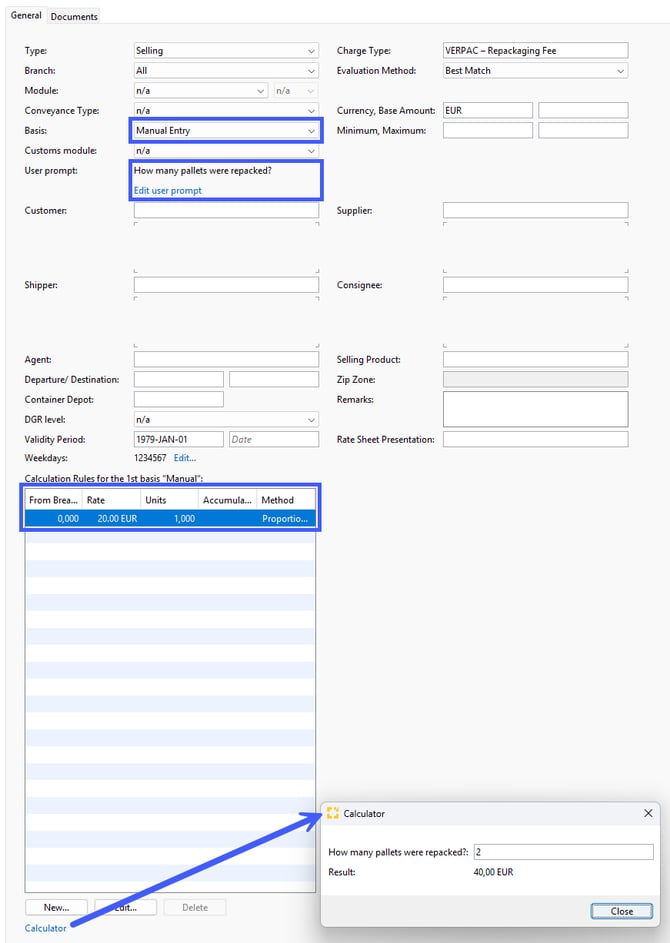
Basis: Manuelle Eingabe
Beispiel: You had to repack some pallets for your customer and want to charge him 20.00 EUR per pallet.
You can find an overview of all available bases here
